

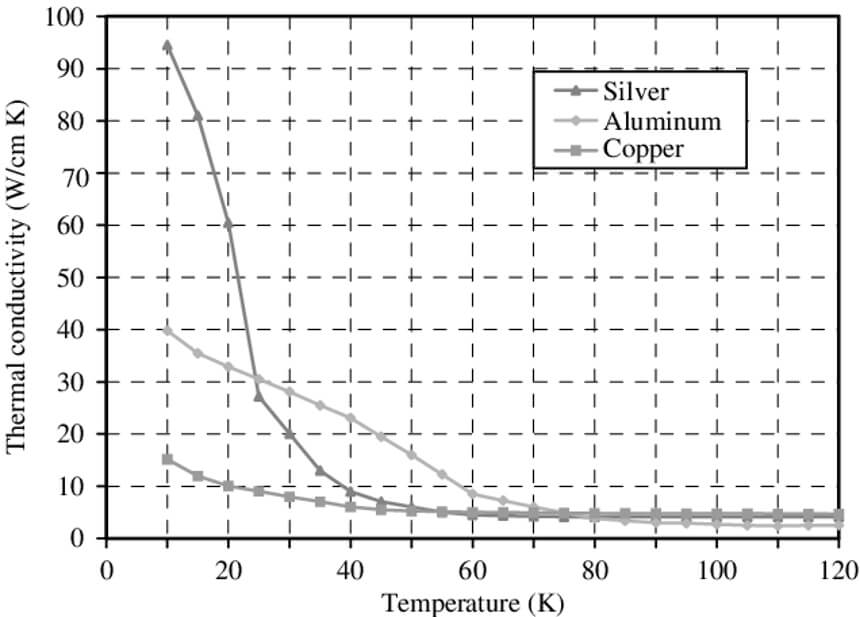
Copper is probably the oldest metal because it has been used to make weapons and other tools since at least 3500 years BC. It has high thermal conductivity, so it requires preheating even for joints that are moderately thick. Its thermal expansion property means that copper can be distorted during welding if you don’t use the proper techniques.
Copper welding is fairly easy once you understand the right procedures for the various methods used to weld copper. Copper is sometimes welded with other metals to strengthen it and to improve its resistance to corrosion. We have explained the different types of copper welding and how copper welding differs from other metals. For instance, it requires twice as much heat as the one used to weld the same size of steel. We have also included a step-by-step instructional guide on how to weld copper.
The speed of welding will mostly depend on the method you are using and the type of shielding gas. MIG welders are faster than TIG welding copper, and more suitable for tasks that require speed. Also, helium allows for faster welding than argon does.
Copper requires preheating at high temperature, unlike copper alloys and metals such as aluminum and bronze. The temperature depends on copper thickness and the method you are using to weld copper. Generally, welding copper requires twice as much heat as welding steel of the same size. It is important to choose the appropriate temperature for the metal you are working on because different temperatures alter the mechanical properties Trusted Source The Effects of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) Welding On The Mechanical Characteristics With Heating Treatment inn S45c Steel Steel material has been used mainly for making tooling, automotive components, other household needs, power generators to frame buildings and bridges. iopscience.iop.org of different metals in varied ways.
The joint design for copper is wider than the joint design of steel and other metals. This is because it has high thermal conductivity and the wider distance allows for better fusion and penetration.
There are a variety of methods on how to weld copper. We will discuss each of them in detail so you can understand how each technique works.
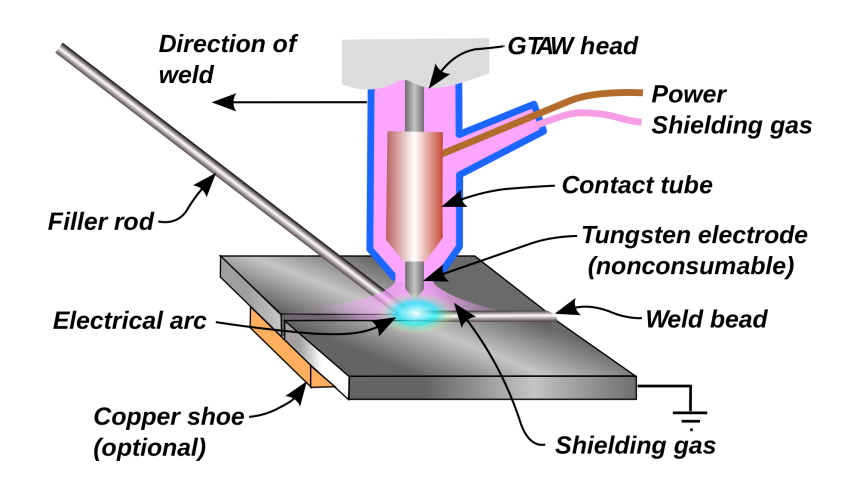
Shielding gas like helium or argon is applied at the tip of the torch to protect the molten copper from deteriorating due to exposure to air as it cools and solidifies.
You use GTAW machine such as Miller Electric TIG Welder,Maxstar to weld copper sections of maximum thickness of 16mm. Helium gas is ideal for welding pieces that are thicker than 1.6mm whereas argon shielding gas is the suitable choice for copper that is up to 1.6 mm in thickness.
A mixture of argon shielding gas and helium is also utilized in thicker copper sections because it is faster and it allows for deeper perforation. The ratio of argon to copper in this mixture is 25%: 75%. Helium is excellent at perforation and argon has great arc stability. If you are using this mixture on copper with stringer beads or narrow weave, we recommend using forehand welding where you point the electrode in the direction of weld movement.
The next method of welding copper is Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) which is also referred to as MIG welding. The process uses an electrode for filler material, similar to SMAW (shielded metal arc welding) technique. The difference is that the former uses a solid wire continuously fed to the torch at your preferred speed whereas the latter uses a series of short rods as the consumable electrode.
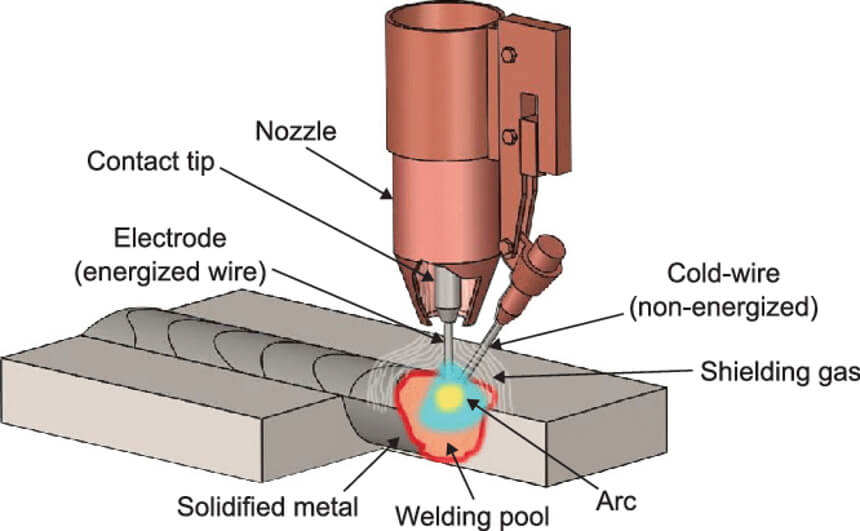
During GMAW, you use spray transfer to deposit the filler material with narrow weave or stringer beads.
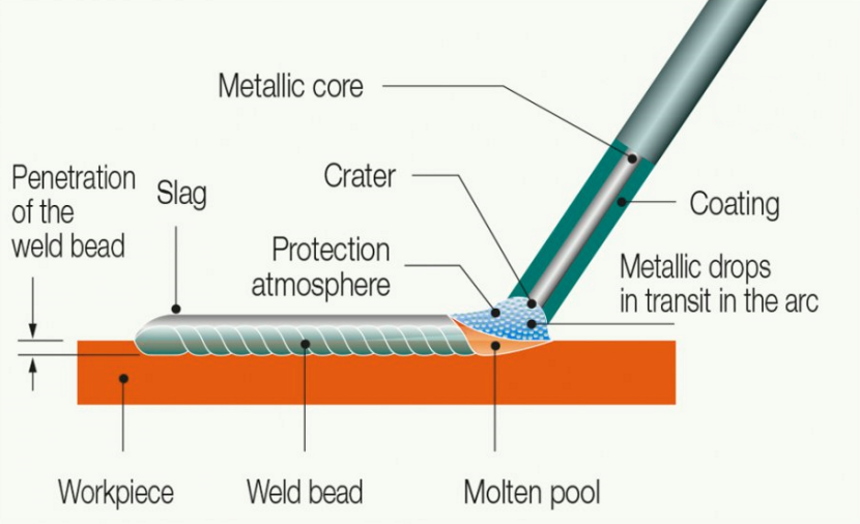
MMAW is mostly used to repair thin copper, to weld joints with limited access, and to weld copper to other metals.

A fitting brush cleans the interior of copper fittings for proper contact with the pipe. A sandcloth cleans the exterior of the copper pipe and the ends to about 1/2 –inch past the fittings. Lastly, copper pipe cutters cut the pipe to the desired length and leave a clean straight edge.
The following simple steps on how to weld copper cover preparation, the actual welding, how to clean up, and the best position for welding.
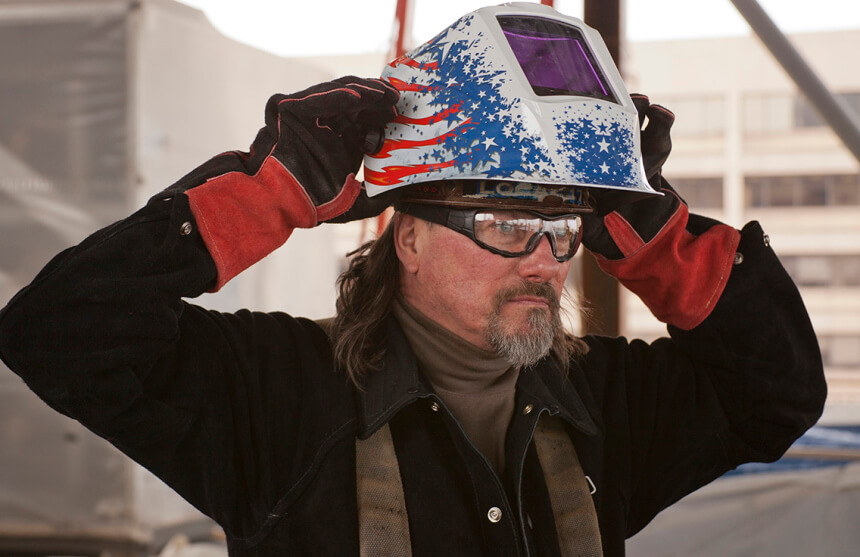

First, you need safety gear such as eye protection, a respirator mask and leather gloves to avoid toxic gases Trusted Source Welding, Cutting, and Brazing - Hazards and Solutions Health hazards from welding, cutting, and brazing operations include exposures to metal fumes and to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. www.osha.gov or an electric shock when handling copper which is a good conductor of electricity.
Secondly, have on hand a fire extinguisher or a spray bottle of water to put out any fire.
The third item you need is a fire retardant cloth that acts as a barrier that prevents fire from spreading to the surrounding environment.
Also, keep away any flammable items.
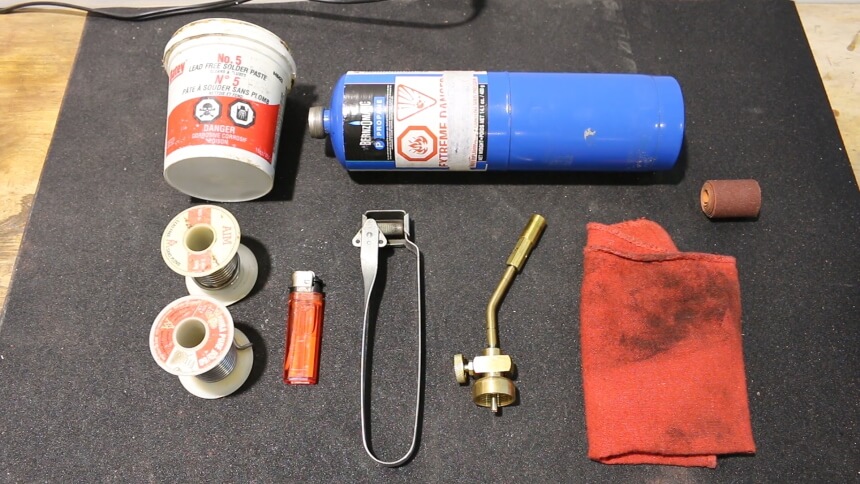
Lastly, ensure you have the soldering tools ready. You can buy kits with a set of basic welding tools.
Due to its high thermal conductivity, copper should be preheated, especially for thick pieces. The temperature varies according to the welder, the method and the thickness of copper, and it ranges from 50° F to 752° F. Keep the preheat temperature until you complete welding the joint to reduce the risk of cracks
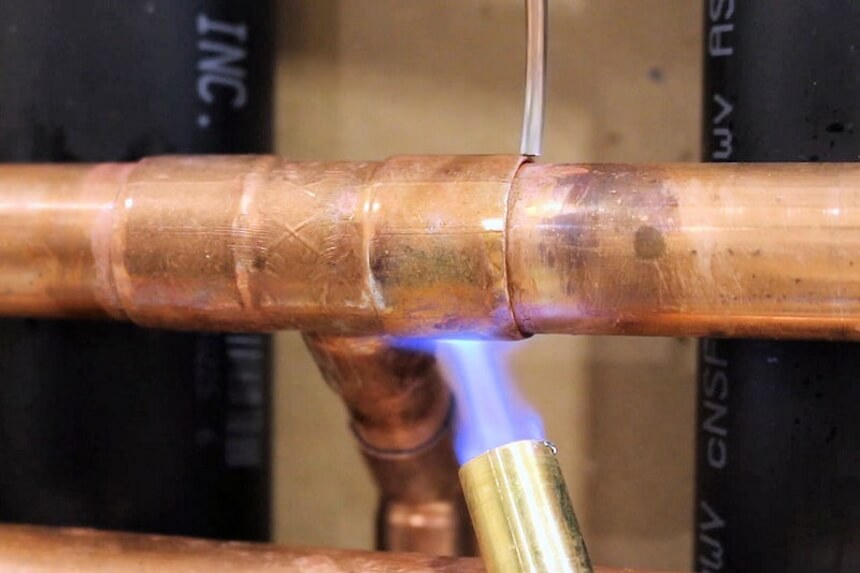
When welding copper pipe, you localize the heat to prevent copper from losing its pliability.
While thicker copper must be preheated at very high temperature, copper alloys do not require preheat because they have lower thermal diffusivity. Metals that do not need preheat are bronze, aluminum and copper nickel alloys.
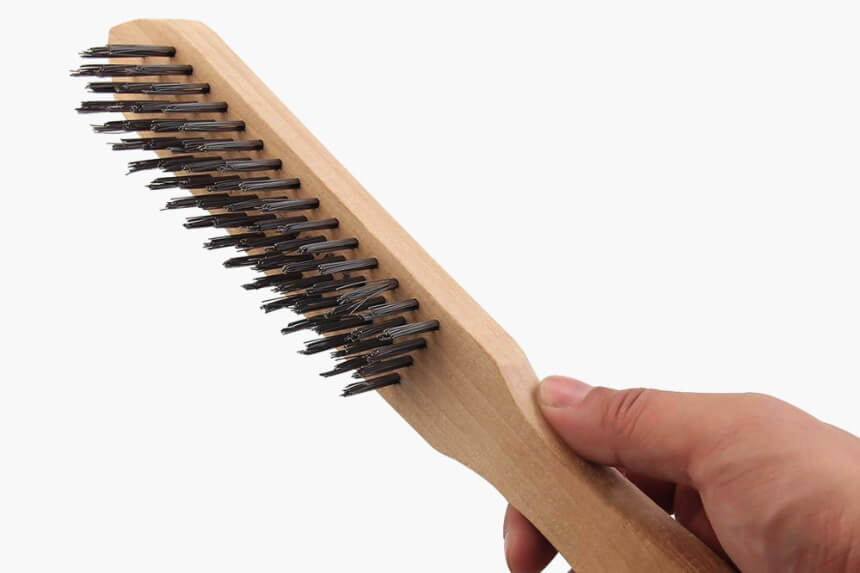

Clean the copper, and then clean the weld area with a bronze wire brush and an appropriate de-grease cleaning agent.
Also, you should use a wire brush to remove oxide film after every weld run is deposited.
Consider a distance of 0.04 to 0.20mm between the joints. The ideal distance is based on copper and the type of brazing alloy. Compared to steel, copper has wider joint designs so that its high thermal conductivity can allow for proper fusion and deeper penetration.
Next, consider a joint overlap that is three times thicker than the thinnest copper section you want to join.
If you have used flux, remove it completely to prevent weakening the joint. You can do this by brushing it off with wire and steaming or rinsing with hot water. You may also dilute it by dipping it in hot caustic soda.
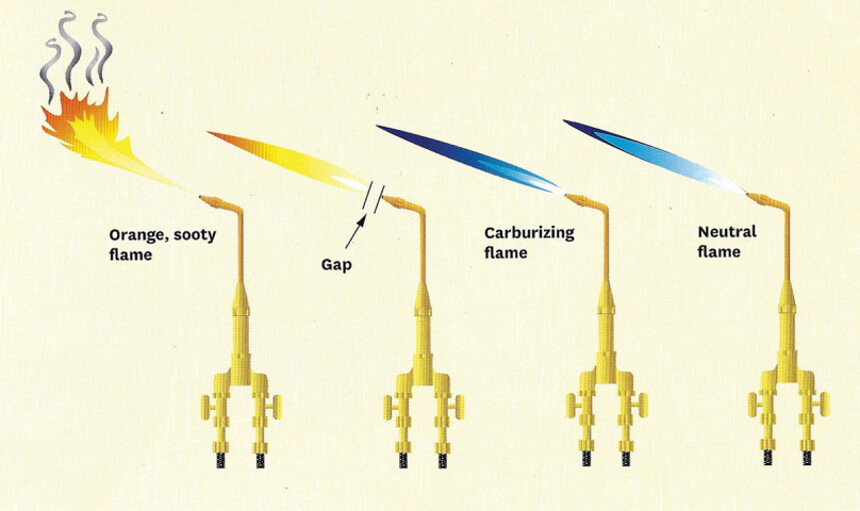
Next, ensure the white inner cone of the oxidizing flame is sharply defined with little to no acetylene haze.
A key consideration you must keep in mind is how to weld copper with the right filler material that will produce copper that is sturdier than the base metal. The filler material depends on the working temperature, the desired joint strength and the resistance of the metal to corrosion.
We recommend using filler material with manganese or silicon content to serve as deoxidant. Both are commonly used for GTAW, MIG welding copper or manual metal arc welding.
Filler materials that are popular for welding copper pipes are ErCu which promotes fluidity and ErCuSi-A which is a better choice for hard-pitch copper and P-oxidized copper.
There are three major techniques on how to weld copper. The appropriate method of welding will depend on your application and the filler material. It also helps to have a welder like Forney Easy Weld 261 that is easy to set up and operate.
The best shielding gases to use when welding copper pipes are argon, helium, or a combination of both. Although helium is more popular, the shielding gas you choose will depend on the thickness of the copper piece.

Our comprehensive guide on how to weld copper has covered everything you need to know about the tools and the process. We have explained the characteristics of copper that makes it different from other metals, how welding copper differs from welding copper alloys and other metals, and the three main methods of copper welding which include MIG welding and arc welding copper. We have also listed all the steps involved in copper welding. The stages include safety measures, surface preparation and the welding procedure. We added other factors such as filler material, joint design and flame adjustment which you should consider when copper welding. All you need to do is to keep these basic steps in mind and to choose the best multiprocess welder that can perform various welding tasks.