
Whether you have ever indulged in welding or not, you may have come across the term duty cycle. It may also be indicated on a welder’s specifications. So, what is the duty cycle in welding? It basically refers to the time you can run the machine safely. This is because welding machines are subject to extreme temperatures that may lead to damages were it not for the duty cycle.
Additionally, there are numerous materials that welding applications may serve. The best welders for aluminum offer exceptional speed and precision for utmost welding results. Continue reading this article to get the necessary information about the duty cycle in welding, its applications, and how to calculate it.
Having got an overview of the duty cycle in a welding machine, let’s take a deep look into the concept. Almost every machine requires cooling down, and welding machines follow suit. But welding machines are customized to automatically switch to thermal overload once they get to high temperature.
Nonetheless, different machines have discrete duty cycles changes based on amperages. For instance, the Hobart 500559 Handler 140 MIG Welder has a 20% duty cycle at 90 Amps. A machine with a 30% duty cycle at 200 Amps will operate for 10 minutes, where the first 3 minutes will be continuous welding, and the last 7 will switch to cool down. This is a crucial aspect in welding machines that prevents damage and increases the machine’s life span. The machine restarts itself when at safe and cooler temperatures.
According to J. O. Milewski Trusted Source Microstructural Evaluation of Low and High Duty Cycle Nd: YAG Laser Beam Welds in 2024-T3 Aluminum | American Welding Society | Welding Research Supplement Journal The propensity for hot tearing and porosity in pulsed Nd-YAG laser beam welding of 2024-T3 aluminum was observed to vary with “beam on” duty cycle. app.aws.org , low and high-duty cycles have an impact on machine performance. This is because when a machine executes at higher amperages output, it heats fast, which reduces the duty cycle. Conversely, if you are wondering how to increase the duty cycle of a welder, using lower amperage power will boost it because low amperages escalate the duty cycle as the machine gets exposed to lower temperatures. Experts who weld at high amperages should dwell on the top-rated MIG welders ideal for DIY and pro metalwork.
We now understand what does duty cycle means and its impact on higher and lower amperages operation. Understanding the different types of duty cycles that will ensure you have a seamless time running your machine. They include:
S1 duty is the first and simplest type of duty cycle. In this operation, the motor operates for a longer duration before getting to thermal equilibrium. The duration when the machine is powered has a notable effect when determining its temperature. S1 duty is efficient, dependable, and simple as it allows the system temperature to stabilize when near or at its designated capacity.
S2 duty is the second type of motor duty that operates with a constant load, just like the S1. However, it shuts off before getting to its equilibrium. Furthermore, cooling off takes longer in S2 and is accompanied by the number of minutes in the duty cycle (S2 30 minutes).
These comprise of cycles with and without rest and entail duty cycles between S3-S8. It also incorporates starting, electric braking, and altering speeds. The machine does not attain its thermal equilibrium, and periodic duty is categorized into two, namely:
It is the simplest form of periodic duty with recurring cycles that have a duration of adamant load and rest periods. Intermittent periodic duty mimics the S2 but does not attain ambient temperatures while at rest.
It comprises a pattern with starting, constant load, and electric braking with no rest periods. Other episodic duty cycles such as S4-S6 and S8-S9 operate the same as S3 and S7 but can execute with or without starting, rest, braking, and loading.
A ResearchGate Trusted Source An equation to predict maximum acceptable loads for repetitive tasks based on duty cycle: evaluation with lifting and lowering tasks | ResearchGate Recently, an equation was developed to predict maximal acceptable effort (MAE) for repetitive tasks based on the product of task frequency and effort duration (ie. duty cycle). www.researchgate.net study affirms that the duty cycle equation is identical, but there are other elements that can cause variance in a duty cycle test. They include:
Although most welding machines are accompanied by a chart from the manufacturer, a duty cycle calculator is an essential tool for getting a precise duty cycle estimate.
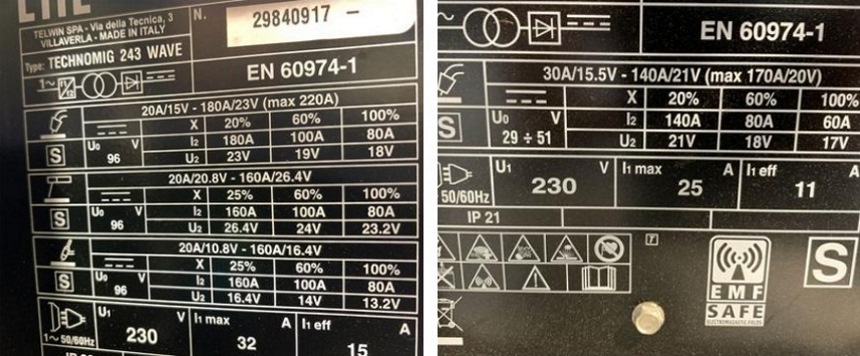
The most preferred form of testing is the European Standard (EN60974-1). This is because it is demanding and gauges the machine performance in reference to real-life conditions rather than estimations of a controlled aura. The Australian Standard (AS609974-1) was derived from the European Standard and can also conduct calculations.
You are required to heat the machine until it gets to the desired temperature by continuous welding. Perform the test in a controlled enclosure that has been heated to 104 degrees Fahrenheit so that it can cut out on the thermal load twice or more. If a machine performs welding at 200 Amps for a total of 3 minutes, it has a cycling duty of 200Amp at 30%.
If a digital signal takes half of the time when powered on and when the other is switched off, it has a duty cycle of 50%. When the test reveals that the duty cycle is above 50%, the digital signal spends more time on the upper state. Nonetheless, when the duty cycle spikes, the more reliable the machine operates.
Some welders have been developed with state-of-the-art technologies to ensure that you get a 100% duty cycle welder. They can also operate at higher amperages, such as 350 Amps to 500 Amps.
Having understood what is duty cycle is in welding and its calculation, below are some of the processes that duty cycle enhances in welding:

The duty cycle is imperative in MIG welding as it determines the continuity of welding without occasional breaks. It is essential to ensure that you work on large orders without numerous periodic delays.
The range of a duty cycle depends on the type of welding application. For example, sheet metal welding requires skill and machines with the best workable duty cycle, enhancing smooth and seamless welds. On the other hand, heavy-duty welding applications require the usage of welders with a bigger capacity to capitalize on welding time.

As opposed to MIG welding, which is an automated process, MMA/Stick welding involves manual processes. There are alternating aspects such as electrodes and slags. The duty cycle does not carry vital roles in MMA compared to MIG, as the operator’s time spent on MMA welding is comparatively less.
The Weldpro Digital TIG 200GD AC/DC machine has a fully capable MMA stick welding function and is fitted with features that go beyond simply welding steel and aluminum.

TIG welding executes detailed tasks which comprise thinner and smaller parts and materials. There are varied roles of the duty cycle in TIG welding because the TIG machine may never get close to achieving its duty cycle limit.
Additionally, the machine does loads of welding with low amperage at a duty cycle of 100%. TIG welding is a manual activity where the operator feeds the filler material by hand, which causes a long and continuous welding process.
The duty cycle has both advantages and disadvantages that can occur when operating your welding machine.
As stated earlier, the cut-out is essential in mitigating the chances of catastrophic occurrences because when the machine attains maximum temperature based on its duty cycle, it kickstarts its thermal overload protection. This automatically switches off the machine, which is vital for its productivity.
It also helps one understand the operation mechanisms of the machine, which is imperative in producing high-quality welds. Additionally, understanding your machine helps get the maximum results with limited defects. It also enables you to have a blueprint of your welding schedule to know when to weld or stop welding.
In case there is a failure in the thermal overload protection, the machine may cause accidents. This may translate to losses and even injuries.
The occasional rests cause delays which may be time-wasting, especially when working on tight deadline tasks. It may cause downtimes, particularly on a machine with a lower duty cycle. Such machines may also subject you to low-quality welds as they attain the duty cycle limit frequently. Below is a table that summarizes the pros and cons of a welder’s duty cycle.
| Pros | Cons |
| Attenuates potential accidents | Fails in thermal overload protection may cause accidents |
| Production of high-quality welds | Frequent delays may cause delays |
| Enables creating a welding schedule | Short spans of welding may cause poor quality welds |

Higher temperatures will escalate the chances of reaching the duty cycle limit faster. Hence, using lower amperages will ensure that your machine is not subjected to extreme temperatures, which spikes the duty cycle of your welder.
The major reason for the duty cycle in welding processes is because it inhibits accidents during a performance. When the duty cycle attains optimal temperature, the thermal overload is triggered, automatically stopping the machine.
Welding machines are customized to prioritize their efficiency and performance needs. Exceeding the duty cycle may cause meltdown due to uncontrollable temperatures, and explosions can be witnessed in extreme conditions.
Welding is an essential scope in life as it supports the performance of numerous industries and spheres. However, understanding what is duty cycle in welding can ensure that you get the best from your machine. It also enhances top-notch welding results due to a regular welding schedule.
This article has discussed how to calculate the duty cycle of your machine. It has also disseminated the information on the effects of dwelling on low and high amperage levels. Some downsides, such as delayed operations, may be encountered due to a lower duty cycle. Additionally, accidents may occur when the thermal overload protection fails to work.





