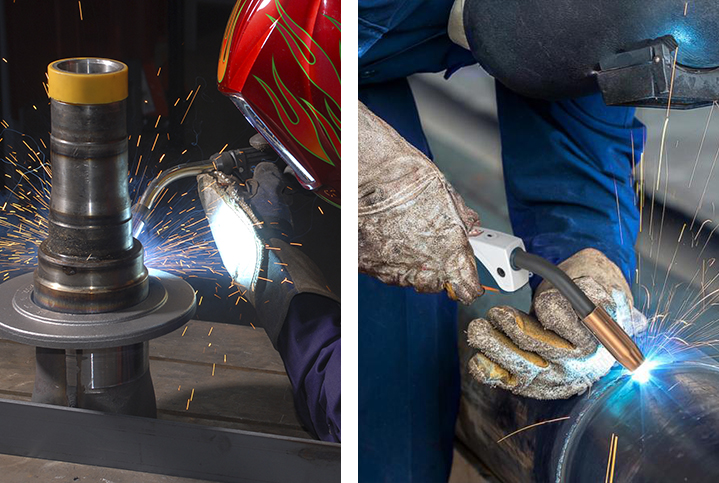

Welding dates back to 3000 B.C. Egyptians learned the art of welding during the Iron Age. The Egyptians combined two pieces of metal by hammering while under heat until they joined. However, in 1881 a Russian named Nikolay Benardos invented carbon arc welding.
After several years of technological developments, welding techniques have evolved to more methods that are straightforward. Currently, there are more than ninety different types of welding. These processes continue with more advanced studies in the transport, building, and nuclear industries. So, what is fusion welding?
People often come across the term fusion arc welding but are unaware of its meaning. So, how do we define fusion welding? Fusion welding involves joining two or more objects by heating. When performing fusion welding, one could use filler materials, depending on the work’s nature. Welders do not apply external pressure when joining the parts.
Fusion welding is different from non-fusion welding. Non-fusion welding takes place under low heat intensity. During this process, the base metal does not undergo any melting process. Welders do not use filler materials when performing non-fusion welding. The best examples of non-fusion welding include soldering, pressure, and brazing welding.
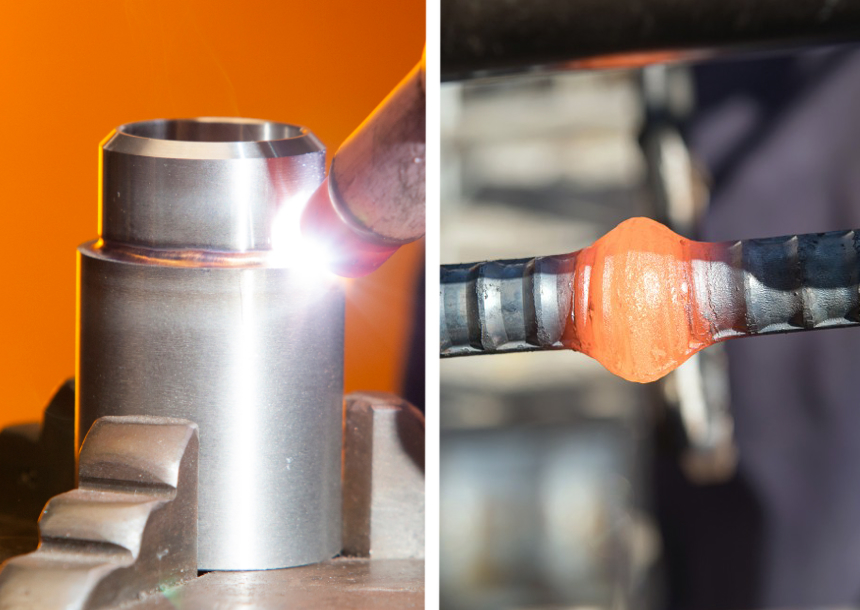

Before understanding fusion welding definition, it is essential to define the term welding. Welding has become an integral part of the building industry. A recent study by the AWS Trusted Source About AWS | American Welding Society The American Welding Society (AWS) was founded in 1919, as a nonprofit organization with a global mission: advancing the science, technology, and application of welding and allied joining and cutting processes, including brazing, soldering and thermal spraying. www.aws.org (American Welding Society) found that welding affects 50% of the U.S. gross product. Welding is a manufacturing process that involves joining two or more identical or non-identical parts using heat. The process might include using a filler or not, depending on the nature of the work.
There are two types of welding
According to the original definition, fusion welding involves joining two edges of similar or different materials using heat. The heat melts the two parts that join together as they cool. In some cases, one can use filler material if the gap between the two parts is extensive. The base material undergoes different stages since the heating process develops a heat affected zone Trusted Source What is the 'Heat Affected Zone' in welding and which types of Welding Processes produce less HAZ? | CWB Group The heat affected zone (HAZ) is that area of metal that has not been melted and has undergone changes in properties as a result of being exposed to relatively high temperatures during welding. www.cwbgroup.org within the materials.
Fusion welding takes part when the molten parts of the base material are combined with the molten filler. It involves applying heat to melt the material on the joining zone or develop a joint externally at the weld point. According to various reviews, the Forney Easy Weld 140 MP is the best equipment for performing different types of fusion welding.
After finding the full definition of fusion welding, it is crucial to understand fusion welding types. The different types of fusion welding are categorized based on the heat source. below are some of the main types of fusion welding:
Fusion arc welding is the most common type of fusion welding. Arc welding involves connecting two or more parts using an electric art. The electric arcs produce high levels above 6000 degrees Fahrenheit using the machines like YESWELDER Digital MIG-205DS MIG welder. This feature makes fusion arc welding ideal for joining hard materials. Welders can also perform arc welding underwater. The most common types of arc welding include:
Some people would refer to it as Oxy-fuel or oxyacetylene welding. This process involves using a blowpipe held in the hand that combines both oxygen and acetylene gas to produce a flare. It is a solvent-based fusion welding that requires a flame to meltdown and connects the surface. Oxygen acts s the primary fuel source for the flame.
This welding type bases its foundation that there must be oxygen to produce fire. The oxygen allows it to create an extremely hot flame that surpasses 4500 degrees Fahrenheit.
High energy welding is a type of fusion welding that uses light radiation to produce heat. Welders blast the radiation on the material’s surface, turning them into a molten state. The two pieces will join once they cool down. The two types of high-energy fusion welding include:
Electron Beam Welding
This high-energy welding uses high-velocity electrons to join two different materials. The process takes place under normal atmospheric pressure, and the electrons produce heat in the material as they enter. The welts are mostly deep and narrow.
Laser Beam Welding
Laser beam welding utilizes a laser beam as the primary source of heat. The use of the laser beam helps maintain a highly focused energy source that is used to join different metal pieces of plastics. It uses light energy to produce heat. The rig produces dissipated light that warms the surface with every single blast.
Resistance welding is one of the fastest fusion welding types. The speed makes it best for use in the automotive industry. Two types of resistance welding include:
Resistance Seam Welding
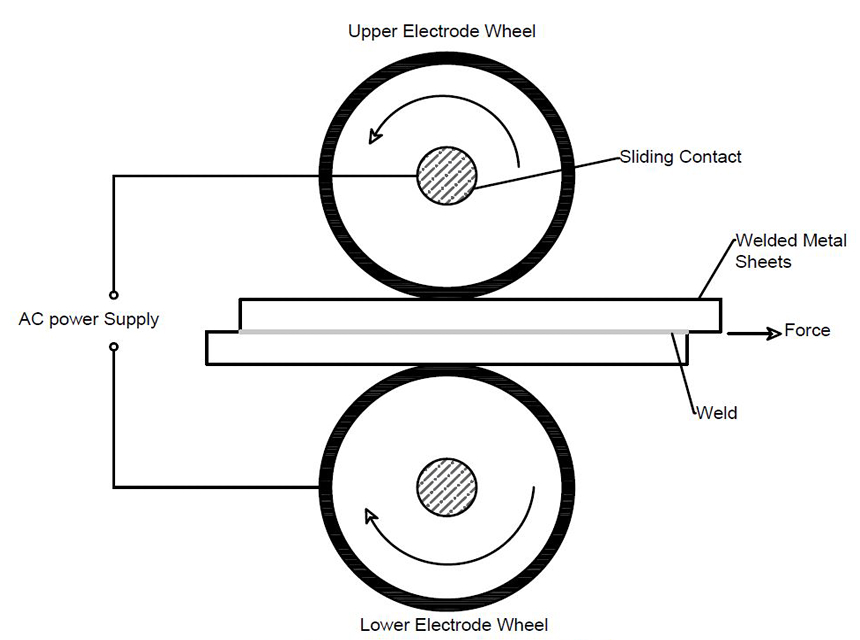
This type of resistance welding involves creating a persistent joint with alternating nuggets. It uses shifting disks to replace the traditional spot welding electrodes as the process goes on.
Resistance Spot Welding
This form of bonding produces heat across two electrodes and depends on the material’s properties and thickness of the workpiece. Welders confine the voltage to a precise spot as the separate workpieces combine concurrently.
Friction welding involves the joining of two different materials using mechanical friction. There are numerous procedures to perform mechanical friction on steel, aluminum, and wood. The process is arduous, but the heat produced is enough to soften and join two separate parts as they cool.
Some of the main types of friction welding include:
During friction welding, one does not require shielding gas, filler, or flux. The process is best for joining light and non-weldable materials such as alloys for aluminum.
Several processes involve the use of fusion welding. Structural engineers use fusion welding when manufacturing large structures such as:
Since it produces high heat levels, one can use fusion metals to combine different materials regardless of their thickness. Some of the main applications include:
Fusion welding involves using high heat levels in joining two or more separate parts. Unlike soldering, fusion welding melts the base metal and may require a filler material to make a joint. High heat exposure turns the metal part into a molten state. These parts join together to form a weld bead as it cools down. The result is always stronger than the base material.
When joining metals, one may need to exert pressure to make welds with a heat source. When joining two metals, shielding gas helps prevent the filler material or joint from contaminating or oxidizing.
Fusion welding is also applicable when joining plastics. Solvent welding uses adhesives instead of heat. Joining plastics using fusion welding takes place in 3 states which include;
Experts use low heat levels when joining plastics since they are softer than metals. One can use internal or external forms of heating.
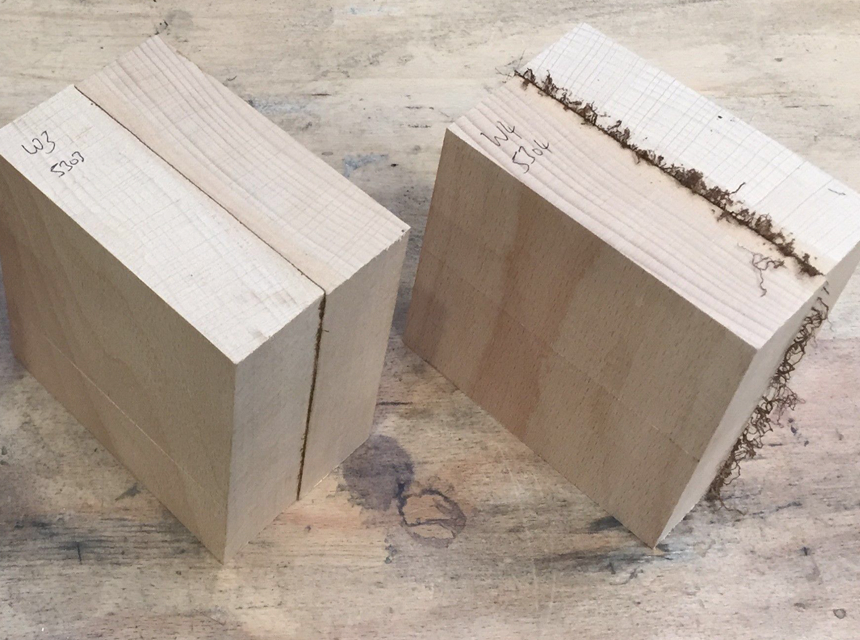
Welding wood parts also require the generation of heat from mechanical friction. The welders expose the materials to intense pressure followed by a linear friction movement that produces heat to bond the two wooden parts.
The process is quick and does not require nails or adhesive to join the two different parts. It also maintains the original design and provides a stronger final workpiece.

Like any other process, fusion welding comes with a fair share of advantages and disadvantages.
First, It is easy to use a filler when the gap between the two parts is large. Fusion does not alter the original shape since no use of external pressure. Also, one does not require to perform edge preparation or design since it may affect heat penetration. In addition, fusion produces a strong joint between the parent materials. This process is quick hence suitable for most industrial processes.
As for the downsides, binding two different materials is difficult, especially when two different melting points. Fusion undergoes some levels of degradation and production of remnant stress since it creates the need for fusion and solidification. More so, the heating process alters the structure of the parent material. Finally, the joined part forms the heat-affected zone that most people view as the weakest point in the structure.
Below is the table of the main advantages and disadvantages of fusion welding.
| Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Fusion welding is a process that involves the use of heat to combine two or more materials. It may require a filler material depending on the nature of the work. It does not need pressure except for resistance welding.
Fusion arc welding uses sufficient heat from a heat source to convert the joining parts into a molten state. Gas and electricity are the most common types of heat sources.
Fusion welding requires high heat intensities that melt the parent material, while non-fusion welding does not involve melting the parent materials hence fewer heat intensities. In addition, fusion welding may require fillers while non-fusion welding does not.
Fusion welding is a common type applied in various industrial and building processes. This process involves using heat to melt and join different parent materials and may require filler material. As said earlier, fusion welding creates a strong bond between the joined parts. The factors that may affect the quality of the fused joint are the size, shape, and relative position of the molten pool, the contact pressure exerted on the workpiece surface, and the cooling methods employed.
One of the benefits of fusion welding is that it can be done at a low cost, making it a reliable option for many industries. The disadvantages of fusion welding are related to weld quality, weld appearance, and the weldability of metals.
We hope now you can answer the question ‘what is fusion welding?’ with the help of this article!





