There are a couple of welder settings you can understand if you set your heart to it. For example, you can learn how to tell how many amps you need for a project. Besides, how many amps does a welder use? There’s no straightforward answer to this question as you’ll soon learn in this article.
Several factors such as material thickness, the field of use, and more determine welder amperage. Needless to say that you must have the correct amount of amperage or you might get your welder and project into trouble. If you struggle with setting the right amperage for your welder, help is here. Read on to learn everything you need to know about welder amperage.
You’re probably aware that some welders seek higher amperage for their projects. They do this because of the several benefits higher amperage offers. We’ll discuss the advantages of higher amperage below:
According to the American Welding Society Trusted Source Amperage The rate of flow of electrons moving in a circuit. It refers to how fast electricity is moving, if at all. awo.aws.org , the number of amps produced by the welder determines the amount of heat available to melt the workpiece and the electrode. With lower amperage, welding thicker materials can be complicated. However, a higher amperage welder can make welding a thicker material a breeze.
Besides, aluminum can be trickier to weld than other metals. Therefore, it’s usually a good thing to have access to the best welders for aluminum that can offer exceptional travel speed, better control, and more.
 Variety of use
Variety of useAnother advantage of a high amperage welder is, you have more options of use. The more power your welder has, the more your range of welding options. Regardless of how you look at it, having a piece of equipment that can do more is always a good thing for a welder.
Ultimately, a higher amperage welder allows you to do more compared to a lower amperage welder. Besides, it helps to have a high-quality multi-process welder around for various projects. Thankfully, the best multi-process welders under $1000 are accessible to help you do the job of three.
There’s no great weld without the right level of penetration. The penetration just has to be right. Unfortunately, it’s harder to penetrate thicker metals, especially with a lower amperage welder. If you can’t get good penetration from a lower amperage welder, trust a higher amperage welder to give you deeper penetration. Moreover, the deeper the penetration, the more likely the weld will hold.
When the power isn’t right, your project is bound to suffer. A lower amperage welder might leave you with some imperfections due to insufficient power. However, a higher amperage welder will provide a consistent and clean weld that makes your project very smooth and presentable. Who doesn’t like clean jobs? We bet no one.
 Welder Amperage by Volt
Welder Amperage by VoltAfter learning the advantages of higher amperage, let’s discuss how many amps a welder needs by volt below:
How many amps does a 110V welder use? Typically, a 110V welder uses about 20 – 30 amps and produces up to 140 amps. While this amperage is not good enough for large projects, it works just fine for small projects around a small shop or home. Plus, most home sockets can support the required amperage.
The next question: how many amps does a 220V welder use? Averagely, a 220V welder uses between 30 and 40 amps. Plus, it produces up to 240 amps and is more ideal for large projects.
Below, we’ll discuss welder amperage by three main types; MIG (Gas Metal Arc Welding, or GMAW), Stick (Shielded Metal Arc Welding, or SMAW), and Arc:
How many amps does a stick welder use? Amperage selection for stick welding is not as complicated as you might have thought thanks to many easily accessible charts that predict the necessary amount of amperage for certain welding thickness levels.
Moreover, you can determine the right amperage yourself by ensuring that your setting is about the same as the rod diameter’s decimal equivalent. For example, a 3/32-inch rod diameter would be 90 amps because of the rod’s decimal equivalent of .094. Another example: a 5/32-inch rod diameter would be 155 amps because of the decimal equivalent of .156.
While this rule of thumb is reliable to a great extent, it’s not absolute but it gives you a great understanding of how many amperes your welder needs.
How many amps does a MIG welder use? MIG welders require different amps based on different applications. For example, you might need a 3-phase welder that could provide between 300 and 600 amps of power for high-end, more efficient production. However, you might not need more than 150 – 200 amps to weld materials with lower thickness levels.
Once you find the right weld setting for the MIG welder (for a certain application), we advise that you write it down on paper and paste it on the side of the equipment to save you from a headache in case you lose your settings.
Moreover, it’s a good thing that you can find reliable and affordable MIG welders on the market. Trust us, you can find high-quality MIG welders under $1000 with multiple process types, great designs, impressive duty cycles, and more.
For example, the Hobart 500559 Handler MIG Welder, which costs less even less than $600, offers two welding processes: MIG (GMAW) and Flux Cored (FCAW). Plus, it welds materials such as aluminum, steel, and stainless steel.
 Arc
ArcThe amperage of arc welders depends on the thickness of the metal sheet you’re working on. For thick metal sheets, 110 amps might be enough for you to get the job done. Thicker metal sheets, on the other hand, may need arc welders with 220 amps and higher. Additionally, the amperage of your arc welder depends on the type of metal and thickness of the metal sheet.
No doubt, arc welders can be pretty easy to use like the beginner-friendly Forney Easy Weld Arc Welder which boasts 120V input and 90 amps output. Additionally, it can handle up to 1/8-inch rods.
 Duty Cycle Considerations
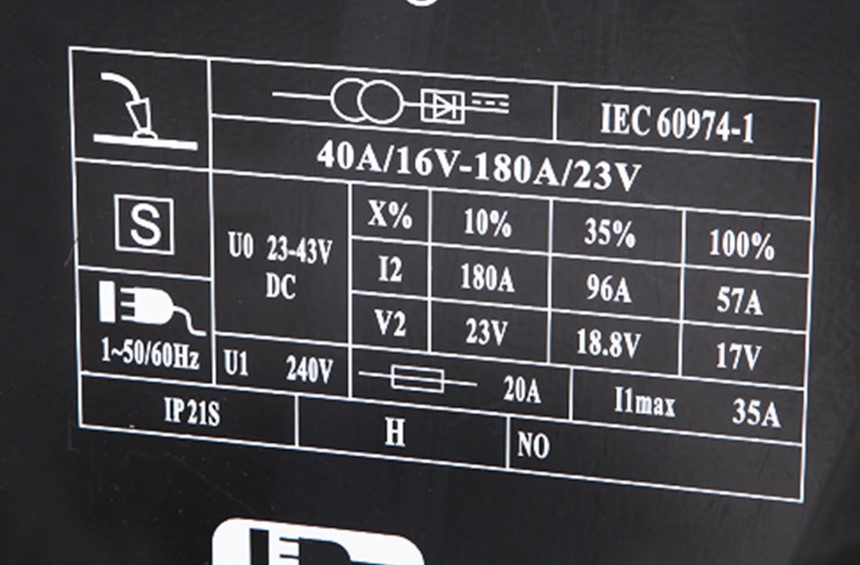
Duty Cycle ConsiderationsBesides metal thickness and other factors you need to consider for welder amperage, the duty cycle is another important consideration. Duty cycle is the length of time the welder can be working during a 10-minute period. As you probably know, some machines are stronger than others. So, it’s not surprising to see some machines with longer duty cycles than some hobby welders.
Generally, the duty cycle is displayed as a percentage. If a welder has 40 percent at 100 amps duty cycle, it can weld continuously for 4 minutes and requires a 6-minute rest before you can begin welding again. Simply put, 10 percent of the duty cycle equals 1 minute of welding time.
 Main problem
Main problemThe duty cycle can be a big stumbling block when you need to weld for longer periods in a row. The frequent stops can quickly frustrate you when you’re working with thick materials on large projects. However, some welders—usually bigger welders that operate on 3-phase power—can work at a 100 percent duty cycle, which is good news although you’ll have to pay more for them.
Welder amperage depends on various factors and we’ll discuss them below:
As you’ve probably learned already, the field of use plays a huge role in determining welder amperage. For example, a large project typically requires higher amperage while smaller amperage is usually good enough for small projects. Essentially, the more demanding the field of use, the higher the number of amps needed.
Material thickness is another factor that determines welder amperage. The thicker the material, the higher the amperage, so that the welder can burn better and penetrate the material.
Lastly, welder amperage depends on power. If you don’t have access to more than 115V in your garage, there’s a limit to what you can weld. However, if you have a 220V welder around, then you’ll have more power to execute your project properly.
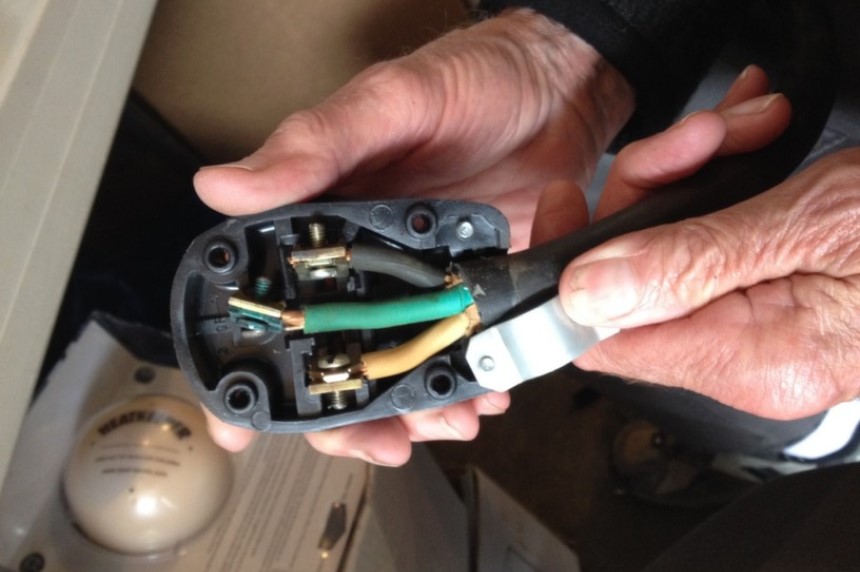

We recommend sizing the welder circuits and wiring based on your welder’s input current requirements. For example, a 40 – 50 input amp welder at 240V will require a 50 amps circuit breaker and 6-gauge wiring. Also, a 30 – 40 amps welder will require a 40-amp circuit breaker and an 8-gauge wire.
Without any doubt, amperage goes a long way in determining the final results of every welding project. Using the wrong number of amps could ruin a welder and the workpiece as you’ve learned in this article. While higher amperage can provide various options, deeper penetration, and consistency, it should only be used when needed.
Besides, amperage depends on a few factors, including field of use, material thickness, and power. If you ever get the question, “how many amps does a welder use?”, this article provides you the right answers for various categories. And don’t forget to wear clean, dry welding gloves, and overalls for safety as advised by the United Kingdom's Health and Safety Executive. Trusted Source Welding: Safety risks from welding The main risk from confined space working is the lack of oxygen. You may be working in an identified confined space, but you should also be aware if your workspace could become a confined space as you weld. www.hse.gov.uk